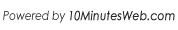Synametrics Technologies
Revolving around the core of technology
AI Assistant in WinSQL
WinSQL version 20 and above offers an AI-assisted chatbot integrated in WinSQL. This chatbot helps users create SQL queries, understand key concepts in relational databases, and provide suggestions based on the current database structure.
Currently, the AI Chatbot is integrated with the following providers:
- Ollama - Free
- Google Gemini - Free tier available
- ChatGPT - Not free.
- Azure OpenAI - Not free.
- Meta Llama - Free (requires signup).
Future versions of WinSQL will provide other providers.
Setting up an AI Assistant
Prerequisite: You must be using WinSQL Professional.
You will see a dedicated tab in WinSQL for AI. The first time you click this tab, it will prompt you to configure it, as shown below.
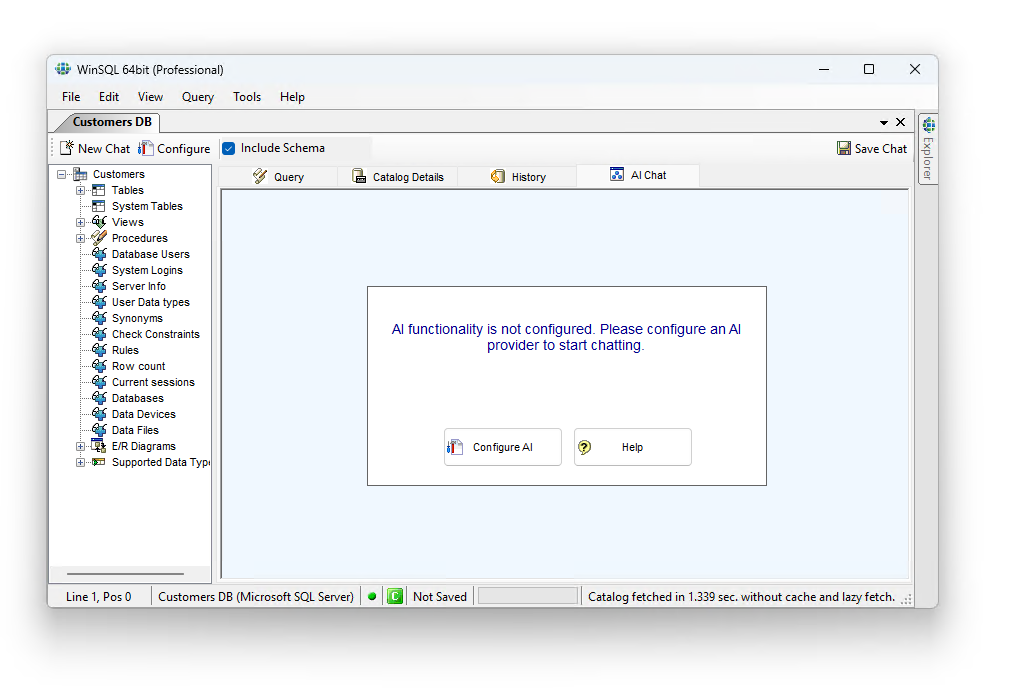
Configuration for every provider is different. Refer to the appropriate links below for your desired provider.
- Ollama - Free
- Google Gemini - Free tier avaialble
- ChatGPT - Paid
- Azure OpenAI - Paid
- Meta Llama - Free (requires signup)
Cost
Synametrics Technologies, Inc. is not associated with any AI provider. Therefore, you must create an account with the desired provider before using it. The cost associated with using AI must be paid directly to the provider.Free Tier
The free tier offered by Google is a good choice to get started with this feature. Although there are limits on the number of queries you can submit in a day, this free tier is sufficient for most users, and the results are very good. All you need to use Google Gemini is to have an account with Google, such as a@gmail.com address.
Data Privacy
When using the AI assistance in WinSQL, sending the design of your database helps the engine return more realistic answers that match your current backend. This, however, can create a privacy concern, particularly for organizations that cannot even risk sharing the database design with a third party.
Keeping such concerns in mind, WinSQL offers the user the option to choose the information they wish to share with the AI provider. This is done by selecting the appropriate value from the Schema Privacy dropdown option.
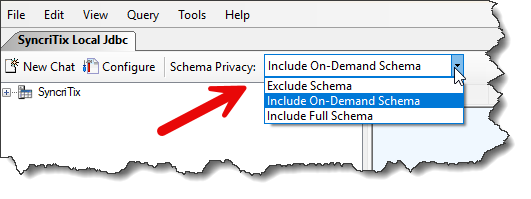
- Exclude Schema
- This is the default. WinSQL will not send any
CREATE TABLEstatements to the AI engine. Therefore, the answers coming back from AI will not apply to your database design. - Include On-Demand Schema
- WinSQL will only send
CREATE TABLEstatements of the objects that appear in your prompt. WinSQL will semantically search your prompt and only send information for the tables that are found. - Include Full Schema
- If selected, WinSQL will send the
CREATE TABLEstatement of every table that is currently available in the Catalog. This option gives you the best answers, but offers the least privacy.
Additionally, WinSQL will only include the design of the tables that are currently visible in the catalog window. Therefore, you can restrict the number of tables sent to the provider by applying a filter for the catalog. Filters are applied by selecting a schema or the starting name of the desired tables, as shown below.
What information is sent to the provider
- CREATE TABLE statements for the tables, provided the Include Schema is checked.
- Name and version of the backend database you're connecting to
- The type of driver (ODBC or JDBC) you're using.
Disabling AI Feature
You can disable the AI feature completely in WinSQL, if required by your company's policies. Please contact our support department via email (support@synametrics.com) for instructions.
Logging
Click Edit > Options, select the tab for Advanced Options, and check the box for Log AI request/response to enable AI specific logging. The generated log file will reside in the $DATA_FOLDER\logs directory.
Examples of using AI in WinSQL
Using AI with a SQL querying tool like WinSQL offers a number of benefits, primarily by making database interaction more accessible, efficient, and powerful for both technical and non-technical users. It essentially acts as a highly knowledgeable assistant for your database.
Here are a handful of examples:
Natural Language to SQL
The most significant benefit is the ability to generate complex SQL queries from natural language prompts (e.g., "Show me the top 10 customers by total sales for the last quarter"). This democratizes data access, allowing business analysts, managers, and other non-technical users to retrieve and analyze data without needing to know a single line of SQL. For developers, this can speed up the process of creating initial queries.
Automated Query Optimization
AI can analyze your generated or existing SQL queries and suggest improvements for better performance. It can identify inefficient joins, missing indexes, and other common performance bottlenecks. This helps you write more efficient queries that run faster and put less strain on the database server, which is especially critical in production environments with heavy workloads.
Steps
- Write your SQL script in the editor
- Highlight the desired part of the script, click the right mouse button and select Explain with AI. If nothing is highlighted, the entire script will be sent for analysis.
Error and Syntax Correction
Enhanced Learning and Explanations
For those learning SQL, AI can be a powerful educational tool. You can ask it to explain a complex query in plain English, breaking down each clause and its function. This helps users understand the underlying logic of the code and become more proficient.
For example, to understand the logic of a stored procedure, select the procedure from the catalog pane, click the node for Procedure Script,
right-click the mouse and select Explain with AI. See image below for an example: